Table of Contents

“Casting”
it is a process in which molten liquid will be allow to solidify in a predefine mould cavity require shape the solidification by braking the mould require shape of the object can be produced.
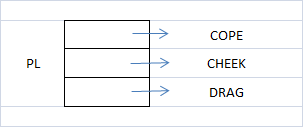
Mould box Of Casting
1. Two Box

2. Three Box
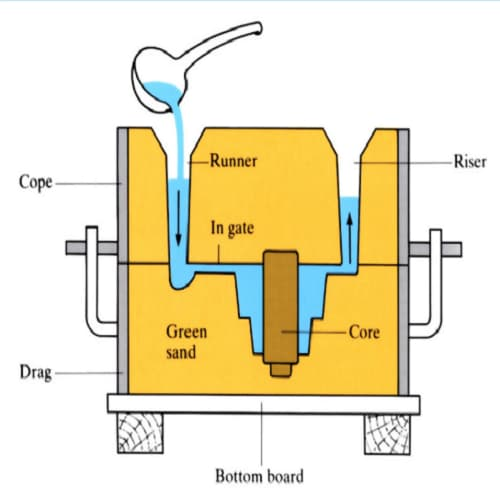
Process Of Casting
- Pattern
- Moulding Sand
- Tools
We can produce following part / application.
- M/C Tool Bled
- Road Roller
- Engine Blocks
- Gear Box
Advantages
Limitations
Tp = Tm + ΔT
Tp = Pouring temp.
Tm = Melting temp.
Tm = ΔT = degree of super heat (100°- 250°C)
Selection of manufacturing process will depend on :-
- Shape and Size of Object to be Produced: Describe the desired shape and size of the object.
- Properties Required by the Object: List the specific properties or characteristics that the object must possess.
- Accuracy and Surface Finish Required by the Object: Specify the level of accuracy and the desired surface finish for the object.
- Number of Components to be Produced: Indicate the quantity or number of identical components that need to be manufactured.
- Cost of Object: Estimate the expected cost associated with the production of the object.
Pattern
It is a replica of final casting to be produced with some modification. Modification are in from of allowances.
Allowance
- Shrinkage or Contraction.
- Draft or Taper.
- Machining or Finish.
- Shake or Rapping.
- Distortion or Camber.
Shrinkage Allowance
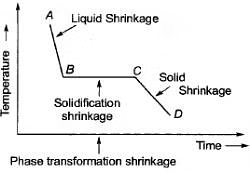
When the liquid metal is allow to solidify there is a possibility of contraction of material during solidification process due to this size of casting decrease.
1. When liquid metal is cooled form pouring to freezing temp the shrinkage is liquid shrinkage
2. During phase transformation process the shrinkage is solidification shrinkage when solid casting is cooled from freezing to ambient temp. shrinkage is solid shrinkage.
Liquid & Solidification shrinkage can be compensated by providing riser there value are express in term of percentage of shrinkage volume. Solid shrinkage can be compensated by increasing the dimension of pattern providing shrinkage allowance these value are express in terms of linear dimension(mm/m).
Solid shrinkage value
- Bismuth = Negligible
- White metal = 5 mm/m
- Cast iron = 10 mm/m
- Aluminum = 13 mm/m
- Copper = 17 mm/m
- Steel = 20 mm/m
- Brass = 23 mm/m
Liquid and solidification shrinkage are maximum for 'Aluminum', which requires more volume of riser.
Solid shrinkage is maximum for brass, which requires a large size pattern.
Total shrinkage is maximum for steel.
Gray cast iron
in case of gray cast iron their is possibility of expansion of material in liquid & solidification state. Due to this no. riser is require this is due to conversation of free from of the carbon into graphite flex (BCC to HCP) In solid state there is a possibility of contraction of material.
Δ V = 2 (% of carbon - 2.8%)% of Carbon > 2.8% expansion
Δ V = 2 (% of carbon - 2.8%)% of Carbon < 2.8% contraction
Draft or Taper allowance
For easy removal of pattern from the mould for the vertical surface of pattern to minimize continues contact with pattern and mould surface draft contact with pattern and mould surface draft or taper allowances is provided.

Machining Or Finish allowance
Casting object are not having smooth surface finish to get smooth finish machining is require due to machining size of casting will decrease to overcome this size of the pattern can be increase by providing machining allowance.
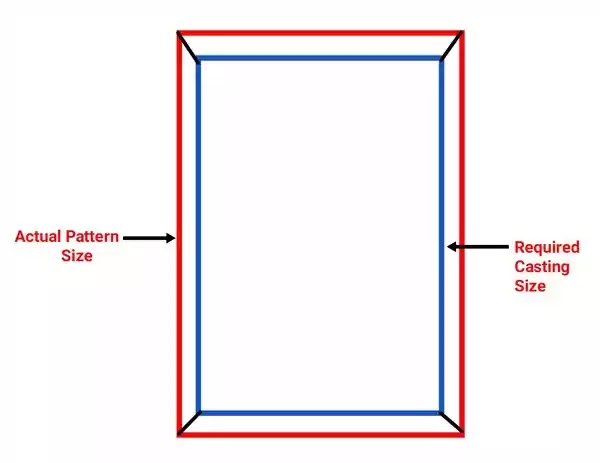
Shake or Rapping allowance
Molding sand will be stick to the surface of pattern due to adhesive property for easy removal of the pattern from mould some clearance is required between pattern and mould surface this can be produced by shaking of pattern. Due to the shaking of pattern size of cavity slightly increases to overcome this size of pattern can be reduced by providing shake allowance it is -ve allowance provided on the pattern.
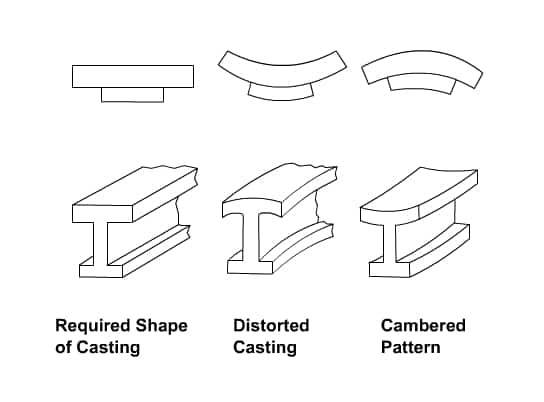
Distortion or Camber allowance
Distortion will takes place out out side due more stress outside (L1>L2) it dep. It is a zero allowance because we are only changing to shape of pattern. Due to difference in linear dimension there is possibility distortion of casting. To overcome this distortion allowance provided on the pattern opposite to the direction of distortion. This values will depends on (l/t) ratio.
So Stay Connected With Us Be Prepared With MECHSTECH.
- Types Of Cutting Tool Materials
- Tool Wear, Tool Life & Machinability
- Parts of Lathe machine
- Various operations possible on the Lathe Machine
- RESEARCH PAPER FIRE EXTINGUISHER DRONE
https://www.mechstech.com/2021/07/types-of-cutting-tool-materials.html
https://www.mechstech.com/2021/07/tool-wear-tool-life-machinability.html
https://www.mechstech.com/2021/06/parts-of-lathe-machine.html
https://www.mechstech.com/2021/06/various-operations-possible-on-lathe.html
https://www.mechstech.com/2021/01/research-paper-fire-extinguisher-drone.html
